- 0731-4007860-3
- +91-8319382426
Treatment We Are Best At
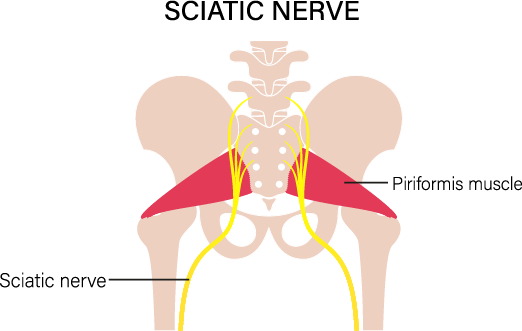
Sciatica
Sciatica refers to pain, numbness, or weakness that occurs along the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the body that runs from the lower back down through the buttocks and legs. Sciatica is typically caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, often due to a herniated disk or bone spur in the spine.
Common symptoms of sciatica include:
- Pain in the lower back, buttocks, or legs that worsens with sitting or standing for prolonged periods of time
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Weakness in the legs or difficulty moving the legs or feet
- Sharp, shooting pain that radiates down the leg
Treatment for sciatica may include medications to reduce pain and inflammation, physical therapy exercises to improve flexibility and strength, and in some cases, surgery to relieve pressure on the affected nerve. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms of sciatica, as it can lead to long-term nerve damage if left untreated.

Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic and often disabling disease that affects the central nervous system, which consists of the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. MS occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the protective myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers, causing interruptions in the transmission of nerve signals.
The symptoms of MS can vary widely depending on the location and severity of the damage to the nervous system. Some common symptoms of MS include:
- Vision problems, such as blurry or double vision
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness, stiffness, or spasms
- Balance problems
- Difficulty with coordination and fine motor skills
- Numbness or tingling in the face, body, or extremities
- Cognitive changes, such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction
There is no cure for MS, but there are a variety of treatments available to help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. These may include medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, physical therapy and exercise to improve strength and mobility, and occupational therapy to help with daily activities.
If you think you may be experiencing symptoms of MS, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
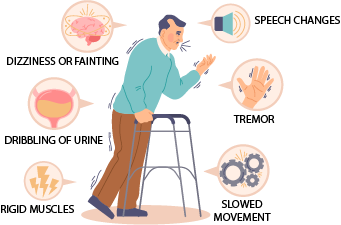
Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects the nervous system. It is caused by the degeneration of neurons in the brain that produce dopamine, a chemical messenger that helps regulate movement and coordination. The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease typically develop gradually over time and can include tremors, stiffness, slowed movement, balance problems, and difficulty with speech and writing.
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease, but there are a variety of treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include medications, such as levodopa, that increase dopamine levels in the brain, as well as physical therapy and lifestyle changes.
It is important for individuals with Parkinson’s disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment may be necessary as the disease progresses.
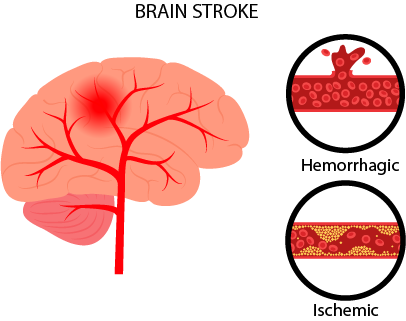
Brain Stroke
A brain stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either by a blockage or a rupture of a blood vessel. When the brain is deprived of blood and oxygen, brain cells begin to die within minutes, which can cause permanent brain damage or even death.
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked by a blood clot, while hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures and bleeds into the brain. Both types of stroke can cause similar symptoms, including sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, severe headache, and trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, and a family history of stroke. Treatment for stroke depends on the type and severity of the stroke and may include medications to dissolve blood clots or reduce bleeding, surgery to repair damaged blood vessels, and rehabilitation to help individuals regain lost function.
It is important to seek emergency medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of stroke, as prompt treatment can help reduce the risk of serious complications and improve outcomes.
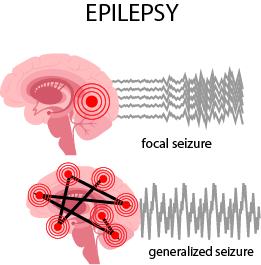
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that is characterized by recurrent seizures, which are caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The seizures can vary in type and severity, and may involve a range of symptoms, such as convulsions, loss of consciousness, or abnormal movements or sensations.
Epilepsy can have a variety of causes, including genetic factors, head injuries, brain tumors, infections, and certain medical conditions. In some cases, however, the cause is unknown.
Treatment for epilepsy typically involves medications that help control seizures, such as anticonvulsants. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove brain tissue that is causing seizures. Other treatment options may include ketogenic diets, nerve stimulation therapies, and behavioral therapies.
Living with epilepsy can be challenging, and individuals with epilepsy may face social, emotional, and practical difficulties related to their condition. It is important for individuals with epilepsy to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. They may also benefit from support and resources provided by epilepsy organizations and advocacy groups.

Vertigo
Vertigo is a sensation of dizziness or spinning, often accompanied by nausea or vomiting. It is a type of vestibular disorder that is caused by a dysfunction in the inner ear, which is responsible for helping the body maintain balance and orientation.
Vertigo can be caused by a variety of factors, including inner ear infections or inflammation, head injury, certain medications, or a disruption in the normal flow of fluid in the inner ear. It can also be a symptom of other underlying conditions, such as Meniere’s disease or vestibular migraine.
Treatment for vertigo depends on the underlying cause, but may include medications to relieve symptoms or treat underlying conditions, vestibular rehabilitation therapy to improve balance and reduce dizziness, or surgical interventions in rare cases.
In addition to medical treatments, there are also a number of self-care strategies that may help manage vertigo symptoms, such as avoiding triggers, practicing relaxation techniques, and making lifestyle changes, such as increasing hydration and getting regular exercise.
If you are experiencing vertigo symptoms, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.

Migraine
Migraine is a neurological disorder that is characterized by recurrent headaches that are often accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraine headaches can be severe and debilitating, and can interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Migraine triggers can vary from person to person but may include stress, certain foods or drinks, hormonal changes, changes in sleep patterns, and changes in the weather.
Treatment for migraines typically involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Medications may include over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, or prescription medications, such as triptans or ergotamines, that are specifically designed to treat migraines. Lifestyle changes may include identifying and avoiding triggers, getting regular exercise, and practicing relaxation techniques.
In addition to medical treatments, there are also a variety of complementary and alternative therapies that may be helpful for some individuals with migraines, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or cognitive behavioral therapy.
If you are experiencing migraines, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals. With proper management, most individuals with migraines are able to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.

Sleep Disorder
Sleep disorders are a group of conditions that affect the ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get restful sleep. There are many different types of sleep disorders, each with its own causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Some of the most common sleep disorders include:
Insomnia – difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Sleep apnea – a condition in which breathing stops and starts during sleep, often accompanied by snoring.
Restless legs syndrome – a condition characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by discomfort or pain.
Narcolepsy – a condition in which individuals experience excessive sleepiness during the day and may have sudden episodes of falling asleep.
Parasomnias – a group of sleep disorders that involve abnormal behaviors or movements during sleep, such as sleepwalking or night terrors.
Treatment for sleep disorders typically depends on the type and severity of the disorder, and may include lifestyle changes, such as improving sleep hygiene, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and regular exercise. In addition, medications or other therapies may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.
It is important to talk to a healthcare provider if you suspect that you may have a sleep disorder, as untreated sleep disorders can lead to serious health consequences, such as heart disease, obesity, and depression. A healthcare provider can help determine the underlying cause of the sleep disorder and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In an emergency? Need help now?
If you are experiencing medical symptoms or have a health concern, don’t wait to get the care you need. Schedule an appointment today with one of the trusted neurologist. With a range of specialties and convenient locations, we are committed to providing you with the best possible care.
